Wi-Fi can't penetrate concrete, metal, etc.
Just like a cell phone in a closed elevator or basement will have poor or no signal.
Our relationships with the Internet are inseparable, in both work and life. If the Wi-Fi connection is unstable or slow, it will obviously affect the quality of using the Internet. The article introduces how to check the 4G LTE sim card router and improve the Wi-Fi signal and quality.
【What's Wi-Fi 】
Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. It is applicable in mobile terminals (laptops, tablets, smartphones, smart appliances, POS, in-car computers, surveillance equipment, etc.) to receive Wi-Fi wireless networks to connect to the Internet.
【 Operational principles】
Wi-Fi stations communicate by sending each other data packets: blocks of data individually sent and delivered over the radio. As with all radio, this is done by the modulating and demodulation of carrier waves. Devices access Wi-Fi through wireless routers to connect to the Internet. Wi-Fi transmits signals by refraction, reflection, and diffraction, and Wi-Fi is transmitted in the air, so it can be blocked by certain substances.
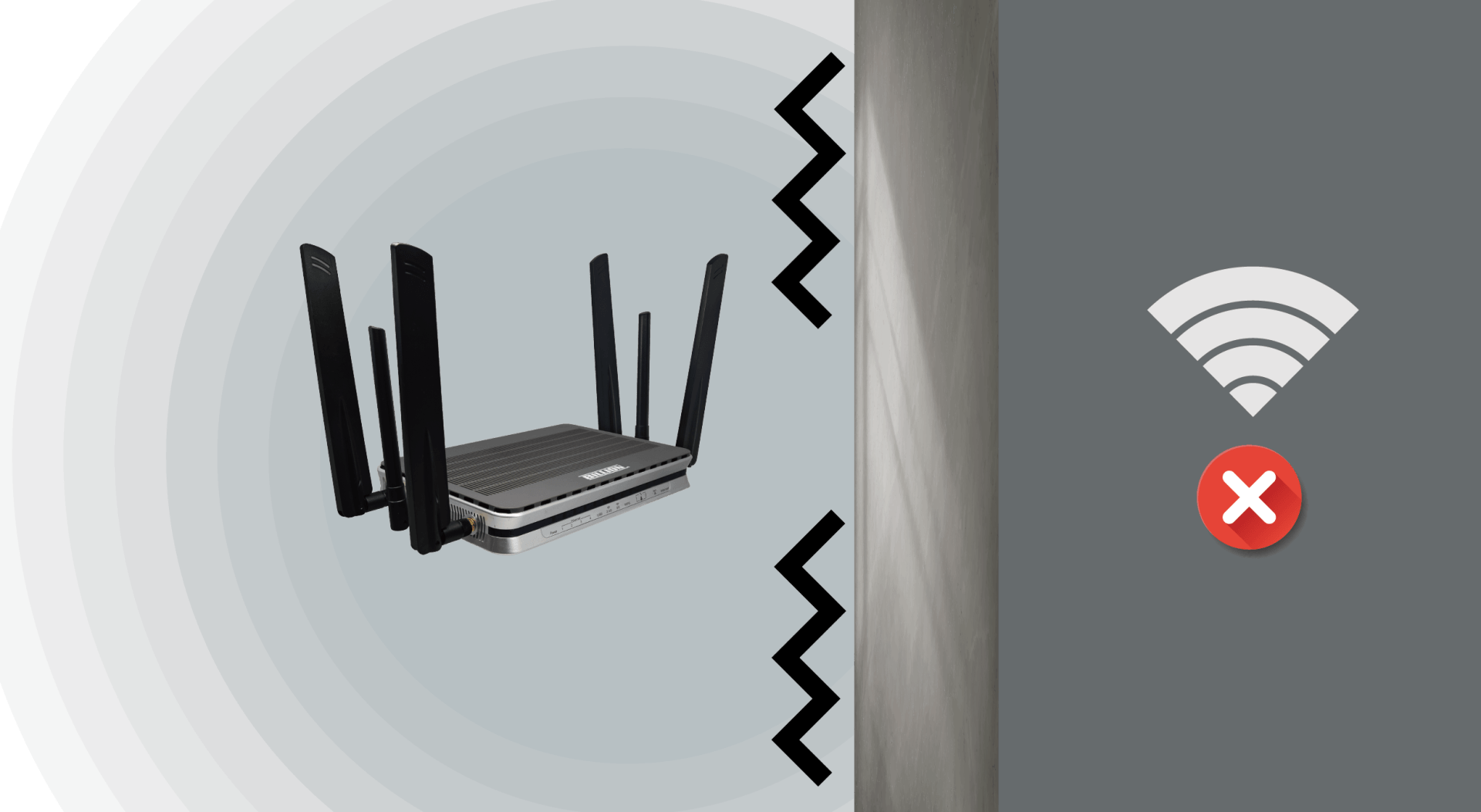

Wi-Fi can't penetrate concrete, metal, etc.
Just like a cell phone in a closed elevator or basement will have poor or no signal.
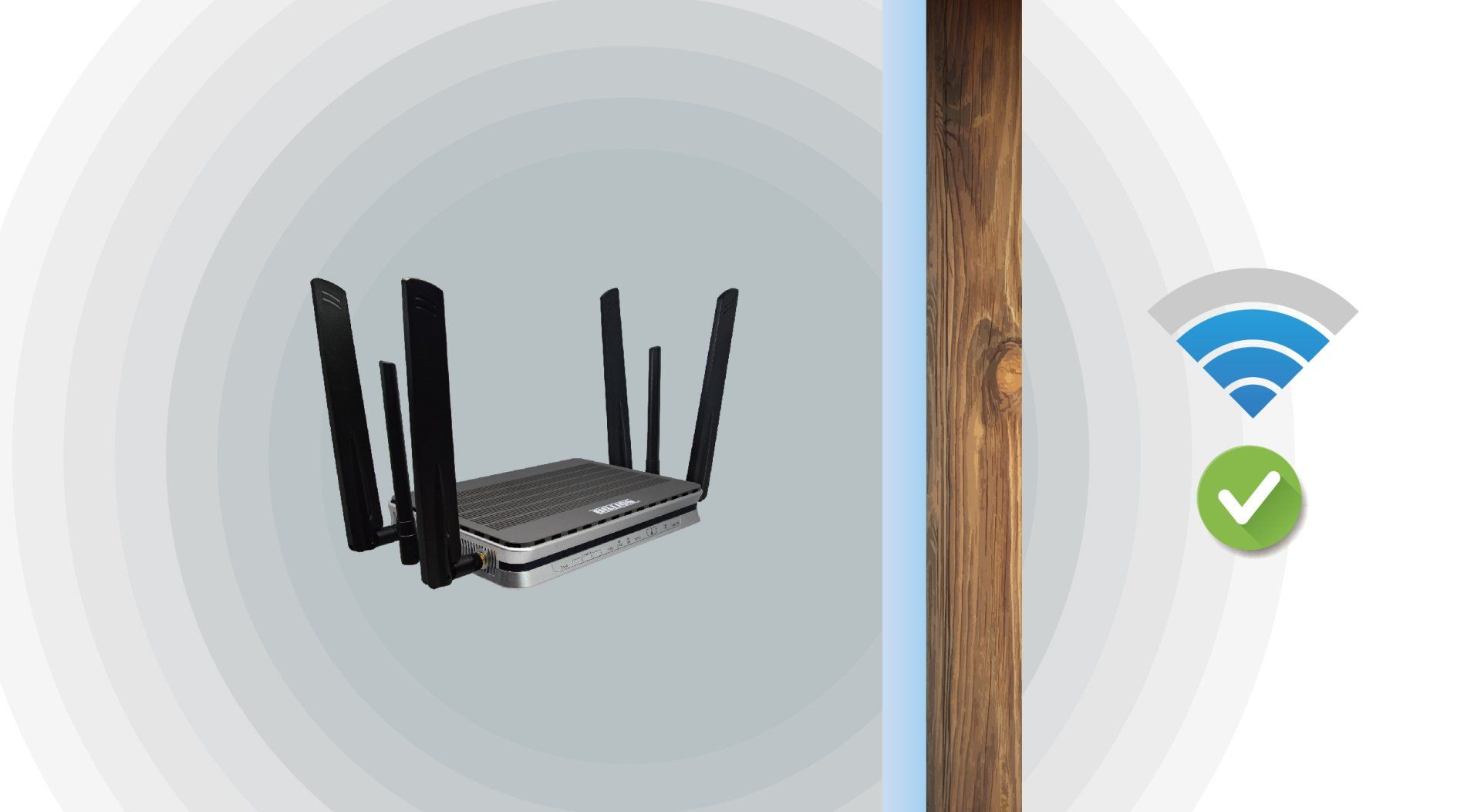

Wi-Fi can penetrate glass, wood, etc. but the signal will be weakened
Some non-metallic materials can be penetrated when used indoors. It is also possible to transmit signals through reflection.
Refraction is the bending of a wave when it enters a medium where the speed is different. For example, glass or water can refract waves. This can play into consideration when you’re carefully placing APs. Different media have different refractive indexes. It’s important to track possible refraction when designing your wireless network because if a signal changes direction in traveling from sender to receiver, this can cause lower data rates, high retries and lead to an overall lessening of capacity.
A wireless signal is just radio waves, which, just like light, can bounce off of certain surfaces. Metal, for one, is a highly reflective material. This is a common occurrence for offices since they are generally complex and intricately designed structures. If a large amount of reflection occurs, signals can be weakened and also cause interference at the receiver.
When waves encounter an obstacle and travel around it, the wave's direction and intensity both change.
While this phenomenon is similar to refraction, it’s more unpredictable. Dust, humidity, unevenness, and other qualities in a material can cause a signal to scatter in all directions. This can have a significant impact on signal integrity and strength.

Wi-Fi spreads out in the direction perpendicular to that of the antennas
Routers are therefore more difficult to transmit signals up and down vertical floors, and walls, if any, can also block them causing signal weakness.
If there is a base station near the carrier and the place where you are using the network, the proximity to the base station also affects the Wi-Fi signal. The frequency bands supported by each carrier also vary.
Some carriers offer plans with speed limit settings. If the frequency of the speed limit is very high, it means that the current plan is not suitable, so you can reevaluate a suitable speed plan.
Suitable for fixed line broadband
The frequent disconnection of the Internet is also related to the type of connection used. If you need stable and high-speed Internet access, fixed line broadband is the best choice.
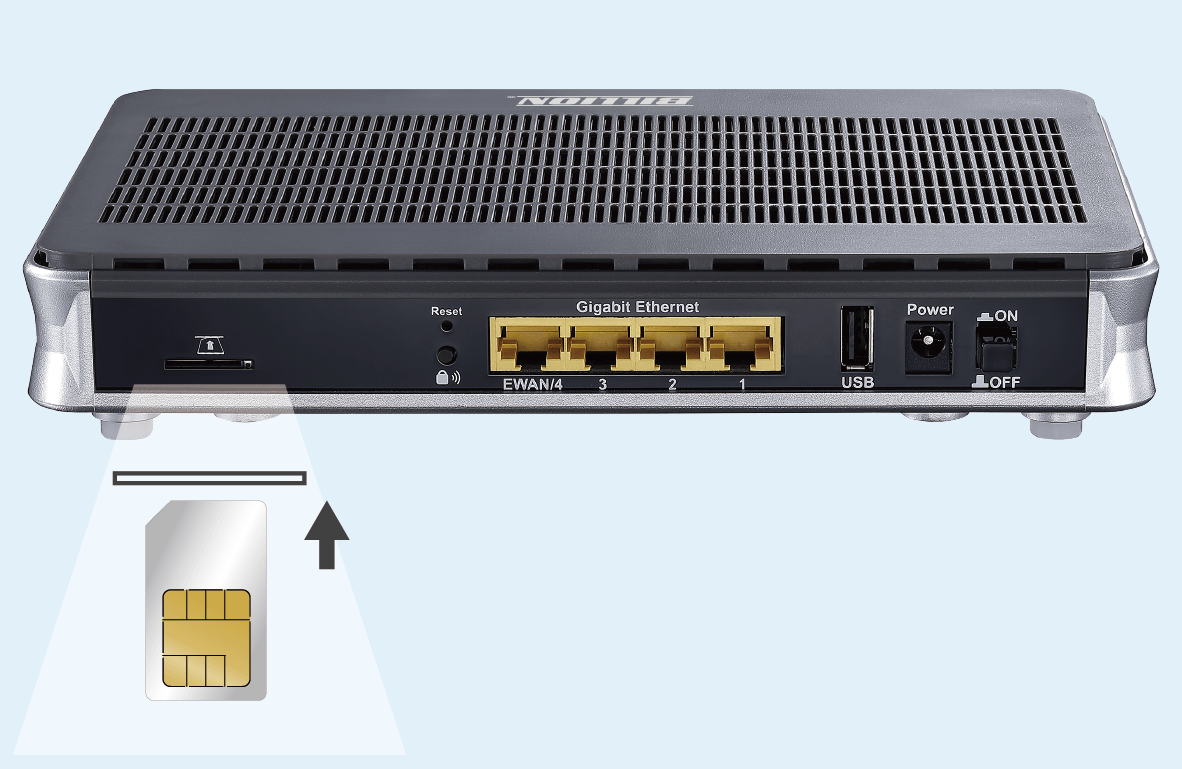
Suitable for mobile wireless broadband
Simply install a SIM card in the router and you can connect wirelessly, which is the most economical way. For general Internet access, few devices, or monitoring network use only, it is recommended to choose a 4G LTE network card router to connect to the wireless network to save the cost of installing a physical wired network.
The bandwidth is fixed. When there are too many iPads/mobile phones/computers/smart home appliances sharing the network, the simultaneous use of these devices may cause network congestion, and the network speed will start to drop.
Solution:
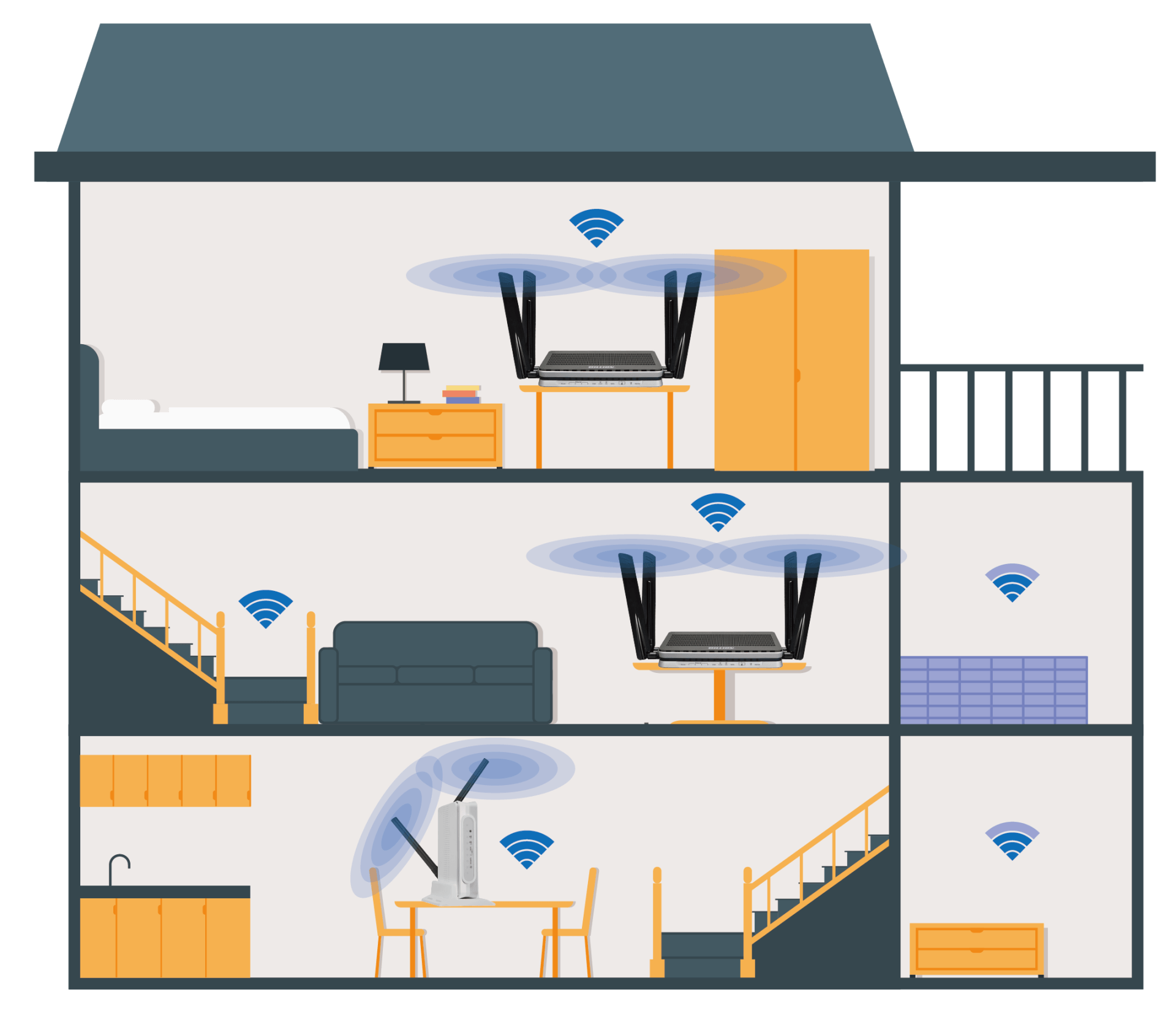
Put the router near the center
Place the router in the center so that the signal can be distributed throughout the house.
For a larger space, you may need to purchase a router or network extender to solve the problem.
✘ Don't do:

Do not put the router in a cabinet
Putting it in a cabinet even if the door is not closed will still block part of the signal.

Don't put the router on the floor
Lift your router up off the ground. Most are designed to broadcast signals slightly downward as they travel from its antenna. Additionally, they can't easily penetrate some solid materials-metal, concrete, and cement-which may be present in your floors.
✓ Do:

Keep the router out in the open
The router's signal can be absorbed by many materials. Don't hide it away in a closet, or stick it in between a big piece of furniture and a wall.
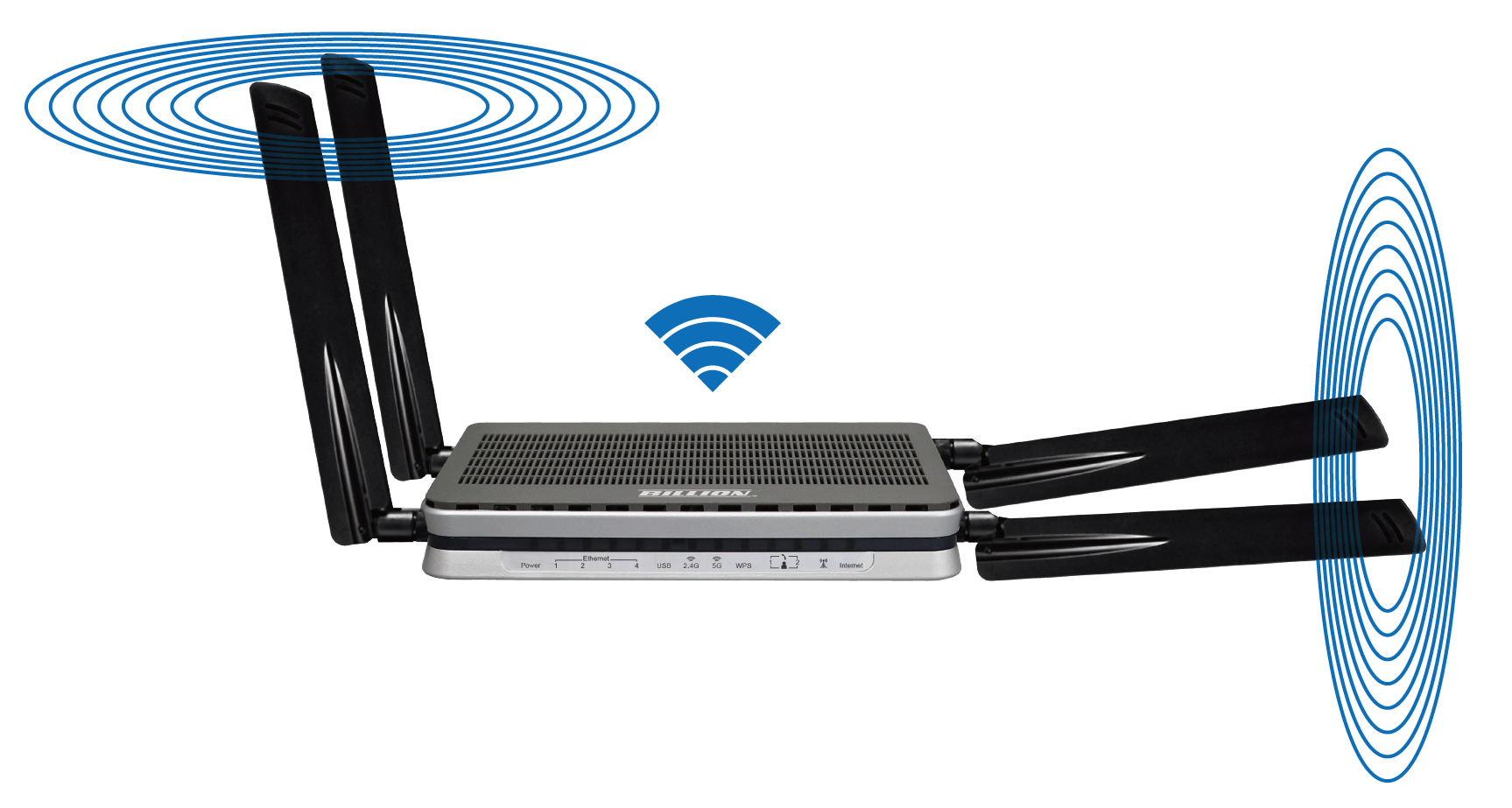
Reposition the antennas
Routers come with one of two types of antennas, internal or external. If your router has two external antennas, try positioning them perpendicular to one another-one pointing vertically and the other positioned horizontally. Most laptops have horizontally aligned antennas inside, but a phone or tablet might be positioned in a different way depending on how you're holding it. Putting one router antenna in a vertical position, and the other in a horizontal, can cover all your bases, while still spreading the signal in your house as broadly as possible.
Measure signal strength
There are a number of apps that allow you to map your Wi-Fi signal, and figure out where it's weak. This can give you some clues on how to better position your router.
Is the Internet usually fast and sometimes slow? Another common cause of Wi-Fi slowdowns is when your neighbors or neighbors all choose the same Wi-Fi channel at the same time, which can interfere with each other and affect the signal of your active wireless network.
Solution:
Log into your router to check whether you are using 2.4G or 5G, and try to change the channel. Since most carriers provide shared broadband, when the number of people sharing the bandwidth reaches a certain level, the network speed will be slow.
(7) Change the Wi-Fi password

Change to a high difficulty password
Using a strong Wi-Fi password is equally important. Default or too simple passwords (e.g. 0000, 1234) can be easily cracked, so it is recommended to replace them with stronger ones.
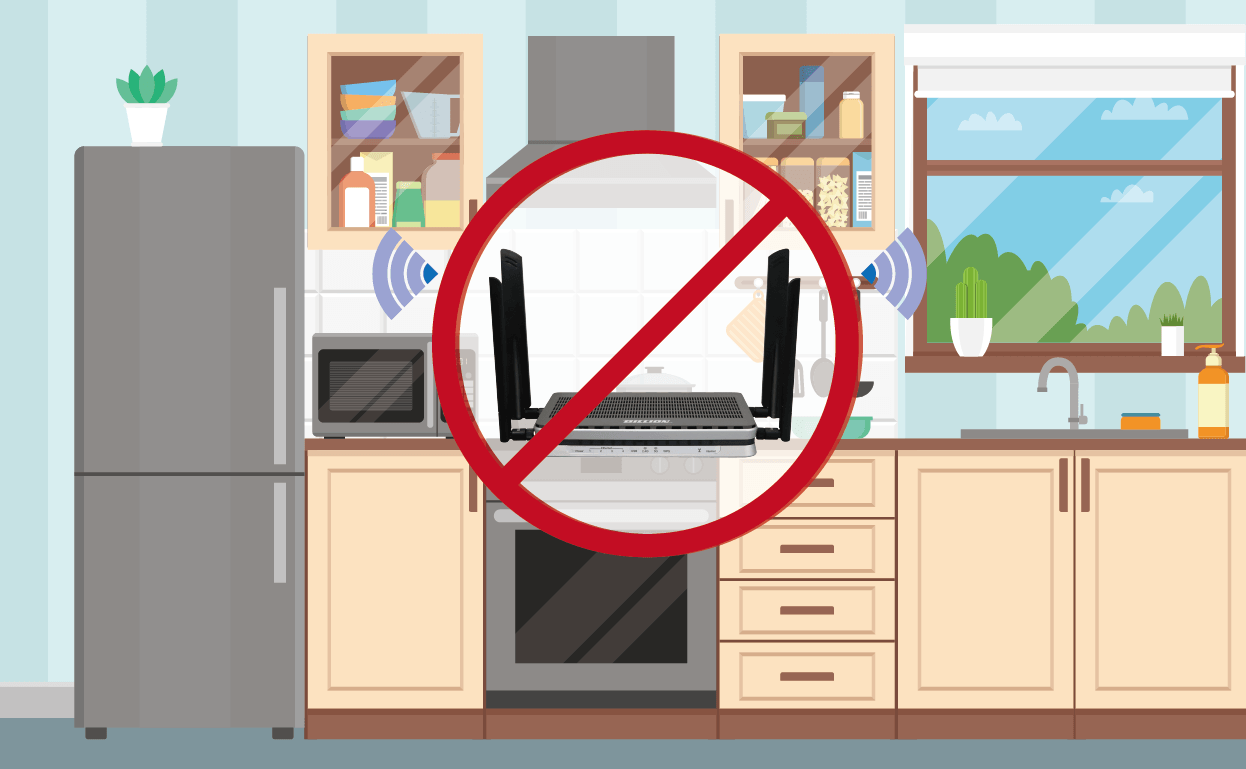
Wi-Fi signals can be weakened as soon as they pass a physical shield, causing sudden slowdowns. Built-in enclosed spaces such as cabinets can also interfere with the weakened signal, and metal and mirrors should be avoided as much as possible.
Therefore, bathrooms/kitchens are not recommended areas to place routers.
(9) Keep the router away from other electronics
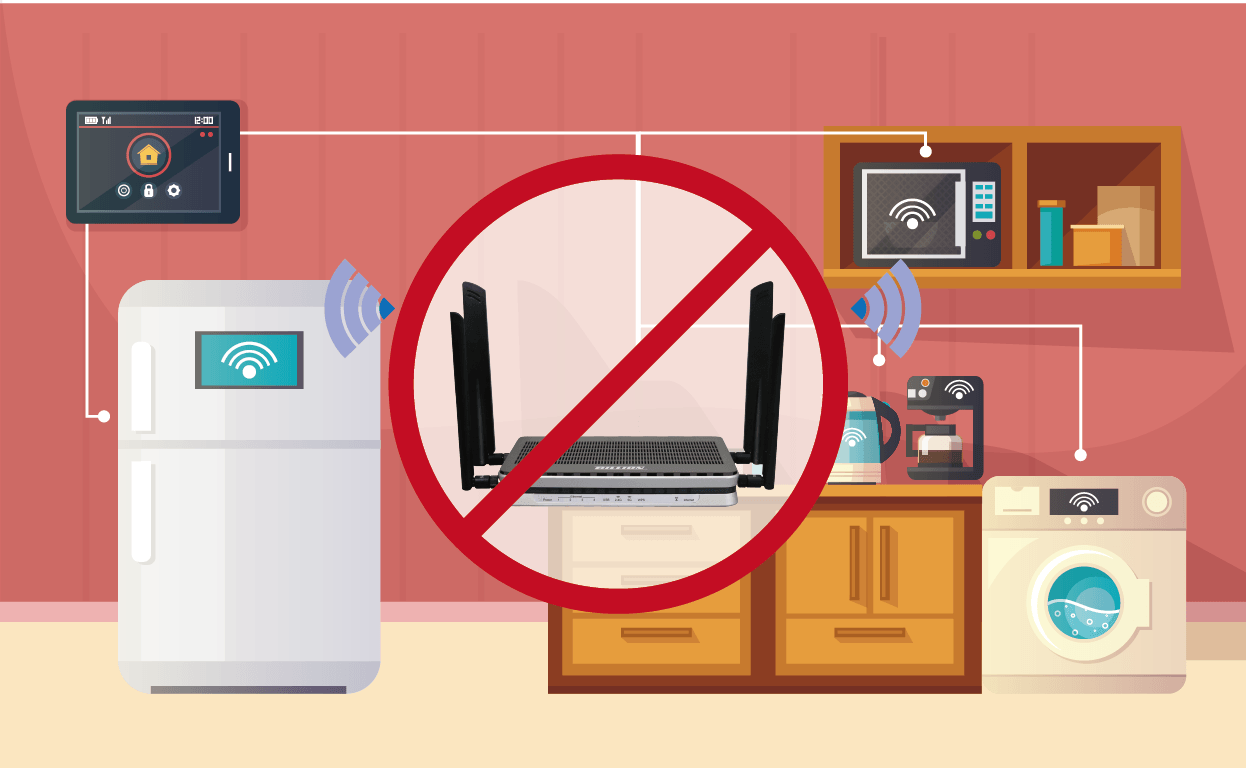
All sorts of electronic devices can interfere with your router's signal: microwaves, TVs, cordless phones—essentially, anything that generates an electromagnetic signal or has a motor. This is why sandwiching it between home entertainment components, beneath your TV, is not a good idea. In general, keep it away from other electronics.
Basically, electronic devices with built-in motors interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Many people are used to placing their routers next to the TV, but if you want better signal performance, it's best to keep them a distance away.
Often a customer will ask the question-How do I know which antenna is best for my application? If a longer antenna has a better effect? Can it amplify the power and increase efficiency?
In fact, the antenna is only responsible for receiving signals and transmitting them. It can be used to change the direction of the signal so that it can be sent to the desired location, but it cannot amplify or make the signal stronger.
Higher gain is not automatically better, it depends on the application. Antennas with gain will lose the vertical propagation or “roundness” of the pattern and become flattened and elongated with a higher gain antenna. The higher the dBi rating, the narrower the reception cone—the nearby signal may become weaker.
Gain and Directivity
The gain of an antenna is simply the measure of an antenna’s ability to direct or concentrate radio frequency energy in a particular direction or pattern. Gain is often measured in dBi and is an important consideration in choosing the right antenna.
The dBi value reflects the antenna's directional/beamwidth characteristics, i.e. directional as opposed to omnidirectional: Generally, the higher the gain (dBi), the narrower the beamwidth—the more directional the antenna.
Difference between dBi antennas

Low gain antennas
If you don't intend to point your antenna in a particular direction, then you don't need much gain; a low gain antenna would provide better signal quality and coverage.

High gain antennas
If you want to focus all of the signal to direct it to a distant target, then a high gain antenna is definitely the best choice.
Choose the antenna according to the application
Higher gain is not automatically better, it depends on the application. Antennas with gain will lose the vertical propagation or “roundness” of the pattern and become flattened and elongated with the higher gain antenna you choose. The higher the dBi rating the narrower the reception cone, the nearby signal may become weaker.
How to choose
Read-around
▶ 9 ways to Improve your Wi-Fi router speed.
▶ How Failover/Failback Function Works?
▶ Choose the Ideal LTE Wi-Fi Router to Experience a Stable & High-speed Connection.
4G LTE SIM card Wi-Fi AP Routers
5G/LTE V/ADSL+2 P2P
Wi-Fi6 AX1500
VPN Firewall Router
5G/LTE V/ADSL+2
Wi-Fi6 AX1500
VoIP VPN Firewall Router
5G/LTE Dual-Babd
Wi-Fi5 AC2400
VPN Firewall Router
LTE Dual-SIM
Wi-Fi5 AC2400
VoIP VPN Firewall Router
LTE V/ADSL+2
Wi-Fi5 AC1200
VPN Firewall Router
| 8207VAZ | 8208AZ | 8206AZ | 5500A | 4520VAOZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 6 AX1500 | ★ | ★ | ||||
| Wi-Fi 5 AC2400 | ★ | ★ | ||||
| WAN Interface | ★ | |||||
| 5G | ● | ● | ● | |||
| LTE | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| V/ADSL | ● | ● | ● | |||
| P2P | ● | |||||
| VoIP | ● | ● |
Copyright © 2026 Billion Electric Co., Ltd. |Privacy Policy